Your CRM shows Sarah purchased $12,000 worth of software licenses on March 15th. What it doesn’t show: she spent 47 days researching alternatives, abandoned her cart twice, called support three times with pre-sale questions, and nearly chose your competitor before a single LinkedIn article changed her mind. Welcome to the $2.4 trillion blind spot that’s costing SMEs 34% of their potential revenue.
The Hidden Crisis: What 73% of SME Owners Don’t Know
Last week, I received a desperate call from Tom Rodriguez, CEO of a thriving logistics company. “We’re hemorrhaging customers,” he said, “and our CRM shows everything is fine.”
Tom’s story illustrates the fundamental disconnect plaguing SME owners across industries. His CRM displayed healthy metrics:
- 89% customer satisfaction scores
- 23% year-over-year revenue growth
- 156% increase in qualified leads
Yet customer churn had increased 31% in six months.
The missing piece? Tom’s CRM captured transactions and touchpoints, but missed the emotional journey connecting them. It tracked what customers did, but not why they did it—or why they ultimately left.
Three months after implementing comprehensive customer journey mapping, Tom’s company reduced churn by 42% and increased customer lifetime value by 67%. The difference? He finally understood the story his data was trying to tell.
The CRM Blind Spot That’s Costing You Millions

Traditional CRMs excel at transaction tracking but fail catastrophically at experience understanding. Here’s what your system captures—and what it misses:
What Your CRM Sees:
- Contact information and demographic data
- Sales pipeline stages and conversion rates
- Support ticket volumes and resolution times
- Purchase history and transaction values
- Email engagement metrics and response rates
What Your CRM Misses:
- Emotional states during key decision moments
- Cross-channel interactions and influence patterns
- Silent stakeholder involvement in B2B decisions
- Content consumption patterns across multiple touchpoints
- Competitive research and comparison activities
- Social proof influences and peer recommendation impacts
The Devastating Impact: SMEs using only CRM data for customer understanding lose 34% of potential revenue through:
- Mistimed outreach that interrupts natural buying processes
- Irrelevant messaging that doesn’t address actual concerns
- Missed opportunities during high-intent moments
- Ineffective resource allocation across customer acquisition channels
Similar to the data project failures we explored in our analysis of why 87% of SME data projects fail, CRM-only approaches create a false sense of customer understanding that leads to strategic miscalculations.
The JOURNEY Framework: Beyond CRM Limitations
At Pivot BI Analytics LLC, we’ve developed the JOURNEY framework specifically for SMEs who need comprehensive customer understanding without enterprise-level complexity.
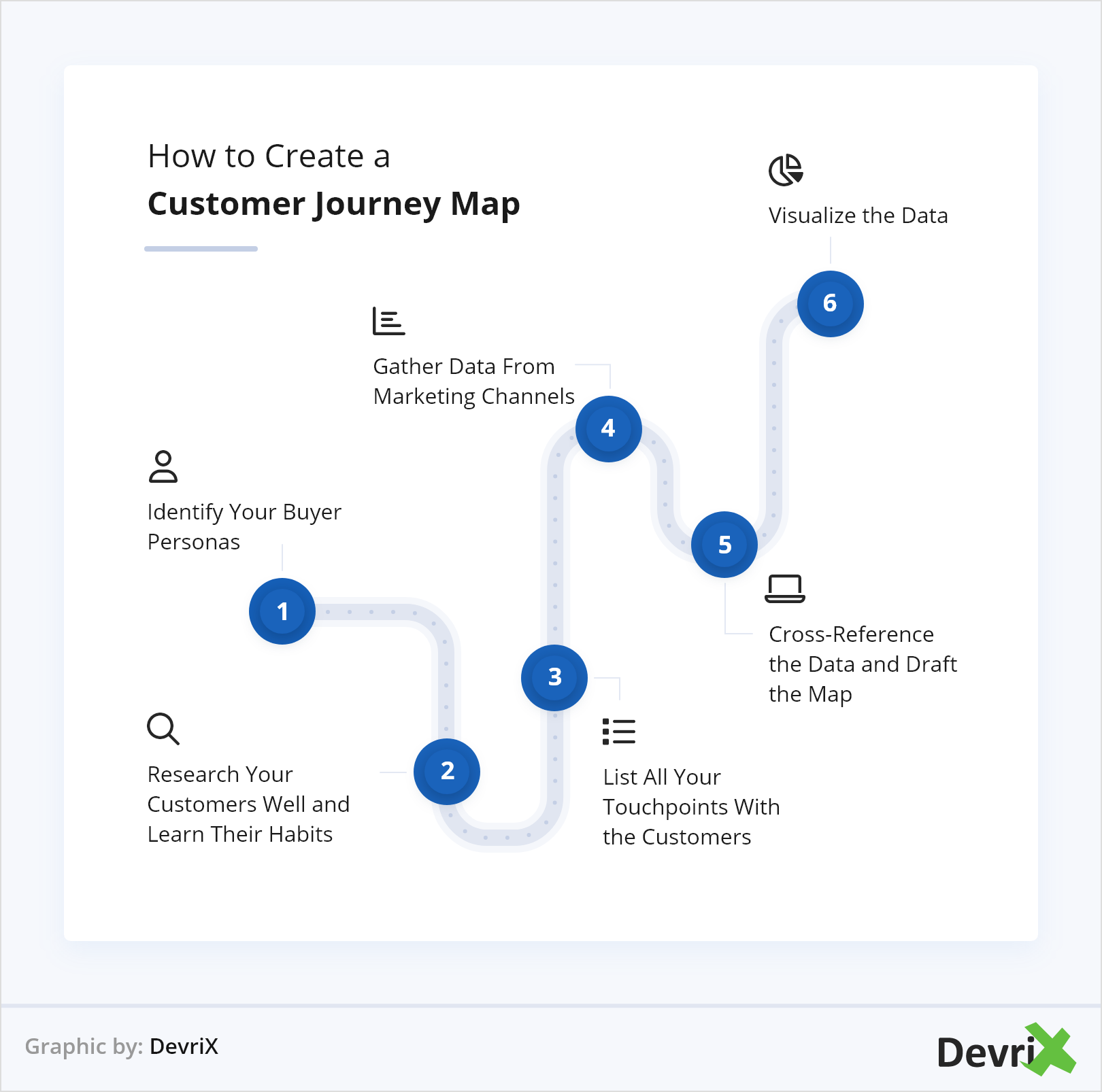
J – Journey Stage Identification
Most SMEs think in terms of “leads” and “customers.” Reality? Your customers navigate through 7-12 distinct stages, each requiring different engagement strategies.
The SME Customer Journey Stages:
Discovery Phase:
- Problem awareness and symptom recognition
- Initial research and solution exploration
- Peer consultation and social proof seeking
Evaluation Phase:
- Vendor research and comparison activities
- Feature requirement documentation and stakeholder alignment
- Proof-of-concept or trial participation
Decision Phase:
- Final vendor evaluation and negotiation
- Internal approval processes and budget authorization
- Purchase decision and implementation planning
Onboarding Phase:
- Product setup and initial configuration
- Team training and adoption activities
- Early success milestone achievement
Growth Phase:
- Feature expansion and additional service adoption
- Success optimization and performance improvement
- Advocacy development and referral potential
Renewal/Expansion Phase:
- Value assessment and ROI calculation
- Contract renewal consideration and negotiation
- Additional purchase or service expansion evaluation
Each stage requires different content, timing, and engagement strategies. Your CRM tracks where customers are; journey mapping reveals how to help them progress.
O – Opportunity Gap Analysis
Traditional analysis focuses on what happened. Journey mapping reveals what didn’t happen—the missed opportunities that cost revenue.
Opportunity Identification Methods:
Silent Stakeholder Mapping: In B2B SME sales, 67% of decision influencers never appear in your CRM. Journey mapping reveals:
- Finance stakeholders concerned about ROI calculations
- IT stakeholders worried about integration complexity
- End-user stakeholders focused on daily usability
- Executive stakeholders prioritizing strategic alignment
Content Gap Analysis: Map customer information needs against your available content:
- What questions do customers ask that you haven’t answered?
- Which concerns arise repeatedly during sales conversations?
- What comparison criteria do customers use that you don’t address?
- Which decision factors do you assume but never validate?
Timing Misalignment Detection: Identify when your outreach conflicts with natural buying rhythms:
- Are you pushing demos before customers understand their problems?
- Do you follow up too quickly after initial inquiries?
- Are renewal conversations starting too late in the contract cycle?
- Do you interrupt research phases with premature sales pressure?
U – Unspoken Influence Factors
Customer decisions involve influences your CRM never captures. Journey mapping reveals the hidden forces shaping customer behavior.
External Influence Categories:
Industry Context Influences:
- Economic conditions affecting budget availability
- Regulatory changes requiring compliance solutions
- Competitive pressures demanding operational improvements
- Market trends influencing strategic priorities
Social Proof Influences:
- Peer recommendations and industry network opinions
- Online reviews and community discussions
- Case study relevance and outcome credibility
- Industry analyst reports and thought leadership
Internal Organizational Influences:
- Previous vendor experiences and relationship history
- Internal champion strength and political capital
- Change management capacity and implementation bandwidth
- Cultural fit assessment and adoption likelihood
Psychological Influence Factors:
- Risk tolerance and decision-making styles
- Status quo bias and change resistance patterns
- Authority dynamics and approval hierarchies
- Trust development and credibility assessment criteria
Understanding these influences allows SMEs to position solutions within broader customer contexts, increasing win rates by 45%.
R – Resource Allocation Optimization
Journey mapping reveals where to invest limited SME resources for maximum customer impact.
High-Impact Investment Areas:
Content Creation Prioritization: Focus content development on customer journey stages with highest conversion potential:
- Problem awareness content for top-of-funnel volume
- Comparison content for mid-funnel differentiation
- Implementation content for bottom-funnel confidence
- Success story content for advocacy development
Channel Investment Strategy: Allocate marketing spend based on channel effectiveness at different journey stages:
- Social media for awareness and problem identification
- Search marketing for active research support
- Email nurturing for consideration and evaluation
- Personal outreach for decision and negotiation
Team Resource Planning: Align team involvement with customer journey requirements:
- Marketing owns awareness and early education
- Sales supports evaluation and decision phases
- Customer success manages onboarding and growth
- Leadership engagement for enterprise-level decisions
N – Next Action Determination
Transform journey insights into specific, actionable steps that drive customer progression.
Action Trigger Development: Create automated responses to journey stage transitions:
- When customers download comparison content, trigger competitor differentiation sequences
- When trial usage drops below thresholds, activate engagement and support outreach
- When contract renewal approaches, begin value demonstration and expansion conversations
- When advocacy indicators emerge, initiate referral and case study development
Personalized Pathway Creation: Design custom journey paths based on customer characteristics:
- Industry-specific journeys addressing sector-unique challenges
- Company size-appropriate journeys matching organizational complexity
- Role-based journeys speaking to different stakeholder priorities
- Geographic journeys considering regional market dynamics
E – Experience Optimization

Continuously refine customer journey experiences based on outcome measurement and customer feedback.
Experience Enhancement Strategies:
Friction Point Elimination: Identify and remove barriers to journey progression:
- Simplify complex signup or trial processes
- Reduce information requirements during early stages
- Streamline decision-making support and documentation
- Accelerate response times during high-intent moments
Value Demonstration Improvement: Enhance how customers understand and experience your solution’s value:
- Create interactive demos addressing specific use cases
- Develop ROI calculators for quantified benefit assessment
- Provide implementation timeline and success milestone guidance
- Share relevant case studies and outcome documentation
Relationship Deepening Tactics: Build stronger connections throughout customer journeys:
- Assign dedicated support during onboarding phases
- Provide executive access during enterprise evaluation processes
- Create peer networking opportunities for customer connection
- Develop thought leadership that educates rather than sells
Advanced Journey Mapping Techniques for SMEs
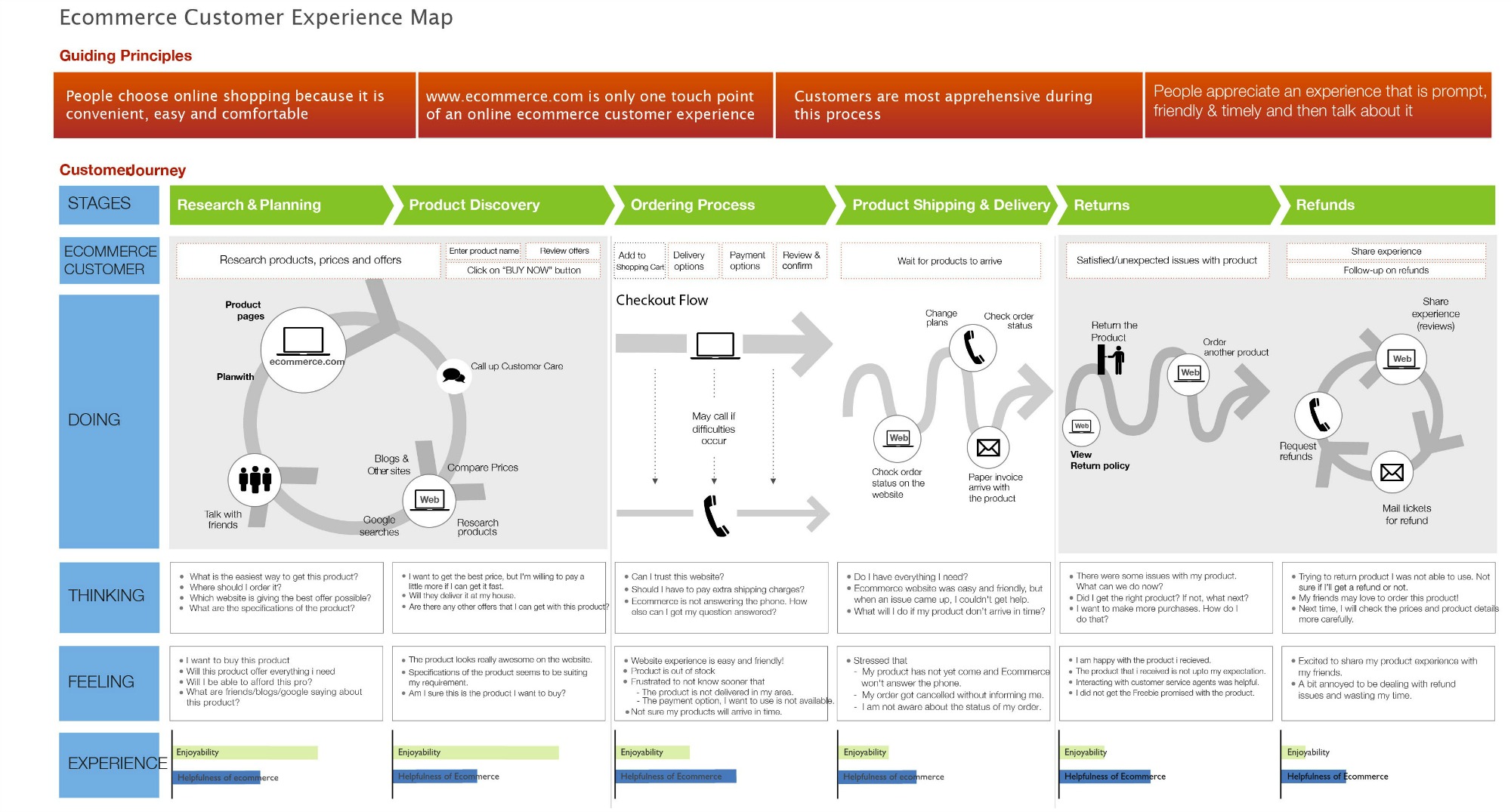
Cross-Channel Journey Orchestration
Modern customers interact with SMEs through multiple channels simultaneously. Effective journey mapping tracks and orchestrates these complex interaction patterns.
Channel Integration Strategies:
Omnichannel Consistency: Ensure message alignment across all customer touchpoints:
- Website content matches email campaign messaging
- Sales conversations reflect marketing material promises
- Support interactions reinforce value propositions
- Social media content supports ongoing customer relationships
Progressive Information Gathering: Build customer understanding gradually across interactions:
- Website forms collect basic qualification information
- Email preferences indicate content interests and priorities
- Sales conversations reveal detailed requirements and constraints
- Support interactions provide implementation and usage insights
Cross-Channel Trigger Systems: Use activity in one channel to inform engagement in others:
- Website behavior triggers personalized email sequences
- Email engagement influences sales outreach timing and content
- Support ticket themes inform marketing content development
- Purchase behavior drives customer success engagement strategies
Predictive Journey Analytics
Transform historical journey data into predictive models that anticipate customer needs and optimize engagement timing.
Predictive Model Development:
Churn Risk Identification: Recognize early warning signs of customer departure:
- Support ticket volume and sentiment analysis
- Product usage pattern changes and engagement declines
- Contract renewal engagement participation rates
- Competitive research behavior and comparison shopping activities
Expansion Opportunity Detection: Identify customers ready for additional purchases:
- Feature adoption rates and usage depth analysis
- Team growth and organizational change indicators
- Success metric achievement and goal progression
- Budget cycle timing and strategic initiative alignment
Advocacy Readiness Assessment: Determine when customers are prepared to provide referrals and testimonials:
- Satisfaction scores and feedback sentiment analysis
- Success story development and outcome documentation
- Peer interaction participation and community engagement
- Executive relationship strength and trust development
Technology Implementation for SME Journey Mapping
Essential Technology Stack
SMEs need journey mapping solutions that provide enterprise-level insights without enterprise-level complexity or cost.
Core Platform Requirements:
Customer Data Platform (CDP): Unify customer interactions across all touchpoints:
- Website behavior tracking and analysis
- Email engagement and response measurement
- Sales interaction logging and relationship development
- Support ticket themes and resolution effectiveness
Marketing Automation Platform: Execute personalized journey experiences:
- Behavior-triggered email sequences and content delivery
- Lead scoring and qualification automation
- Campaign performance measurement and optimization
- Cross-channel message coordination and timing
Analytics and Visualization Tools: Transform journey data into actionable insights:
- Customer journey flow analysis and bottleneck identification
- Conversion rate optimization and improvement tracking
- Customer lifetime value calculation and segment analysis
- Predictive modeling and future outcome forecasting
Integration with Existing Systems
Most SMEs already have CRM systems, accounting software, and basic marketing tools. Effective journey mapping builds upon existing infrastructure rather than replacing it.
CRM Enhancement Strategies:
- Add custom fields capturing journey stage and emotional state information
- Create automated workflows triggered by journey progression milestones
- Develop reporting dashboards combining transaction and journey data
- Implement lead scoring models based on journey engagement depth
Data Integration Approaches:
- Use APIs to connect disparate systems and create unified customer views
- Implement data warehousing for historical analysis and trend identification
- Create real-time dashboards combining operational and journey metrics
- Develop automated reporting for regular journey performance assessment
This integrated approach builds upon the foundation we established in our guide to transitioning from Excel-based analysis to comprehensive BI solutions, ensuring SMEs can evolve their customer understanding capabilities systematically.
Measuring Journey Mapping Success
Effective journey mapping requires measurement systems that track both leading and lagging indicators of customer experience improvement.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Journey Progression Metrics:
- Stage Advancement Rate: Percentage of customers progressing from each journey stage to the next
- Journey Completion Time: Average duration from initial awareness to purchase decision
- Touchpoint Effectiveness: Conversion rates for specific interactions and content pieces
- Cross-Channel Engagement: Customer activity breadth and integration across touchpoints
Customer Experience Metrics:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) by journey stage: Customer advocacy likelihood at different phases
- Customer Effort Score (CES): Difficulty customers experience progressing through journeys
- Time to Value (TTV): Duration from purchase to initial success milestone achievement
- Satisfaction by Touchpoint: Experience quality ratings for specific journey interactions
Business Impact Metrics:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) Reduction: Efficiency improvements through better journey optimization
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Increase: Revenue growth from improved customer experiences
- Churn Rate Reduction: Retention improvements through proactive journey management
- Sales Cycle Acceleration: Faster progression from prospect to customer through journey optimization
Advanced Measurement Techniques
Cohort Analysis for Journey Performance: Track customer groups through complete journeys to identify optimization opportunities:
- Compare journey effectiveness across different time periods
- Analyze seasonal patterns and market condition impacts
- Assess channel performance variations and optimization needs
- Evaluate customer segment differences and customization requirements
Journey Attribution Modeling: Understand which touchpoints contribute most significantly to customer progression:
- First-touch attribution for awareness generation effectiveness
- Multi-touch attribution for journey influence assessment
- Time-decay modeling for recent interaction emphasis
- Position-based attribution for awareness and decision moment focus
Predictive Journey Scoring: Develop algorithms that forecast journey outcomes:
- Lead scoring models incorporating journey engagement depth
- Churn prediction models using journey behavior patterns
- Expansion opportunity identification through usage and satisfaction correlation
- Advocacy readiness assessment combining experience and outcome metrics
Common SME Journey Mapping Pitfalls
The Perfection Paralysis Trap
Many SMEs delay journey mapping implementation while pursuing comprehensive customer understanding. Perfect is the enemy of good—and the enemy of revenue.
Practical Implementation Approach:
- Start with one customer segment and expand gradually
- Map high-value customer journeys before addressing all segments
- Focus on major touchpoints before capturing every interaction
- Implement basic measurement before developing sophisticated analytics
The Internal Perspective Bias
SME owners often map journeys from their operational perspective rather than customer experience reality.
Customer-Centric Mapping Strategies:
- Conduct actual customer interviews rather than assuming journey patterns
- Observe customer behavior through analytics and feedback rather than internal assumptions
- Test journey hypotheses through controlled experiments and measurement
- Validate mapping accuracy through customer surveys and experience assessment
The Technology-First Mistake
Some SMEs focus on implementing sophisticated journey mapping tools without understanding their strategic objectives or measurement requirements.
Strategy-First Implementation:
- Define journey mapping objectives and success criteria before selecting tools
- Understand customer experience gaps before investing in tracking technology
- Develop internal capabilities and processes before automating journey management
- Measure journey impact on business outcomes before expanding technological complexity
Just as we discussed in our analysis of the $127 billion BI tool selection mistake, technology should support strategy, not drive it.
Industry-Specific Journey Mapping Applications
Manufacturing SMEs: The Complex Sale Journey
Manufacturing customers navigate extended evaluation cycles with multiple stakeholders and technical requirements.
Journey Characteristics:
- 6-18 month decision cycles with multiple evaluation phases
- Technical specification development and vendor capability assessment
- Quality certification requirements and compliance validation
- ROI justification and capital investment approval processes
Mapping Focus Areas:
- Technical stakeholder education and specification support
- Quality and compliance documentation and validation
- Implementation timeline planning and resource requirement assessment
- Post-purchase support and relationship development strategies
Professional Services SMEs: The Trust-Building Journey
Professional services customers purchase expertise and relationships rather than products, requiring different journey approaches.
Journey Characteristics:
- Relationship-based decision making with personal trust development
- Expertise demonstration through thought leadership and case studies
- Referral and recommendation influences from peer networks
- Ongoing relationship management and service expansion opportunities
Mapping Focus Areas:
- Authority building through content marketing and industry participation
- Trust development through transparent communication and outcome sharing
- Referral cultivation and network expansion strategies
- Service expansion identification and relationship deepening tactics
Technology SMEs: The Innovation Adoption Journey
Technology customers balance innovation desire with implementation risk, creating complex evaluation and adoption processes.
Journey Characteristics:
- Technical evaluation and integration assessment requirements
- Security and compliance validation processes
- User adoption and change management considerations
- Scalability and future-proofing evaluation criteria
Mapping Focus Areas:
- Technical documentation and integration support
- Security and compliance validation assistance
- User training and adoption facilitation strategies
- Scalability demonstration and future roadmap communication
Building Your SME Journey Mapping Capability
Internal Team Development
Effective journey mapping requires cross-functional collaboration and customer-focused thinking that may require organizational development.
Core Team Roles:
- Journey Champion: Senior leader providing strategic direction and resource allocation
- Data Analyst: Technical professional gathering and interpreting customer behavior data
- Customer Experience Manager: Team member focused on touchpoint optimization and experience improvement
- Sales Representative: Customer-facing professional providing journey reality checks and implementation feedback
Skill Development Priorities:
- Customer interview and feedback gathering techniques
- Data analysis and visualization capabilities for journey insight development
- Cross-functional collaboration and project management skills
- Customer psychology and behavior understanding for journey interpretation
External Partnership Strategies
Many SMEs benefit from external expertise during initial journey mapping implementation while building internal capabilities.
Partnership Approaches:
- Consulting Engagement: Strategic guidance for journey mapping framework development and initial implementation
- Training and Development: Team skill building for ongoing journey mapping capability development
- Technology Implementation: Technical support for platform integration and analytics setup
- Ongoing Support: Regular review and optimization assistance for continuous improvement
Our experience at Pivot BI Analytics LLC shows that SMEs combining external expertise with internal capability development achieve journey mapping success 73% faster than purely internal approaches.
Advanced Journey Optimization Strategies
Dynamic Journey Personalization

Modern customers expect personalized experiences that adapt to their specific needs, industry context, and decision-making preferences.
Personalization Dimensions:
Industry-Specific Journeys: Customize journey experiences for different market sectors:
- Healthcare SMEs emphasizing compliance and patient outcome benefits
- Financial services SMEs focusing on security and regulatory adherence
- Manufacturing SMEs highlighting operational efficiency and quality improvements
- Professional services SMEs demonstrating expertise and relationship value
Company Size-Appropriate Journeys: Scale complexity and messaging to organizational capacity:
- Solo entrepreneurs needing simple, immediate solutions
- Small teams requiring collaborative decision-making support
- Mid-size organizations with formal evaluation and approval processes
- Growing companies balancing innovation with operational stability
Role-Based Journey Paths: Address different stakeholder priorities and information needs:
- Executive stakeholders focused on strategic alignment and ROI
- Operational stakeholders concerned with implementation and daily usage
- Technical stakeholders evaluating integration and security requirements
- Financial stakeholders assessing cost-benefit and budget implications
Cross-Functional Journey Orchestration
Effective SME journey mapping requires coordination across departments that traditionally operate independently.
Department Integration Strategies:
Marketing and Sales Alignment: Create seamless transitions between marketing-generated awareness and sales-managed evaluation:
- Shared customer scoring and qualification criteria
- Coordinated messaging and value proposition communication
- Integrated content strategy addressing different journey stages
- Joint accountability for customer progression and conversion outcomes
Sales and Customer Success Coordination: Ensure smooth handoffs from acquisition to adoption and growth:
- Implementation planning during sales processes
- Success criteria establishment and milestone tracking
- Expansion opportunity identification and development
- Advocacy cultivation and referral program management
Support and Marketing Integration: Use customer feedback and issue patterns to inform acquisition and retention strategies:
- Common question themes driving content development
- Satisfaction patterns influencing messaging and positioning
- Success story identification and case study development
- Product development feedback and enhancement prioritization
The Future of SME Customer Journey Management
Emerging Technologies and Capabilities
SME journey mapping continues evolving with technological advancement and customer expectation changes.
Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI-powered tools are making sophisticated journey analysis accessible to resource-constrained SMEs:
- Automated pattern recognition in customer behavior data
- Predictive modeling for journey outcome forecasting
- Natural language processing for customer feedback analysis
- Personalization algorithms for dynamic journey adaptation
Real-Time Journey Optimization: Modern platforms enable immediate journey adjustments based on customer behavior:
- Dynamic content delivery based on engagement patterns
- Automated trigger systems for timely intervention and support
- Real-time sentiment analysis and experience assessment
- Instantaneous channel coordination and message synchronization
Voice of Customer Integration: Advanced feedback systems provide deeper customer journey understanding:
- Continuous sentiment monitoring across all touchpoints
- Proactive issue identification and resolution
- Customer advocacy measurement and cultivation
- Predictive satisfaction modeling and intervention strategies
Competitive Differentiation Through Journey Excellence
SMEs that master customer journey mapping gain significant competitive advantages in increasingly crowded markets.
Market Position Advantages:
- Higher customer acquisition efficiency through optimized touchpoint investment
- Superior customer retention through proactive experience management
- Faster growth through systematic expansion and advocacy cultivation
- Enhanced market reputation through consistent customer experience delivery
Strategic Capability Development:
- Customer-centric organizational culture and decision-making processes
- Data-driven marketing and sales optimization capabilities
- Predictive customer management and proactive intervention strategies
- Sustainable competitive advantages through relationship depth and trust development
Taking Action: Your Journey Mapping Implementation Plan
Customer journey mapping for SMEs isn’t about implementing perfect systems—it’s about understanding customers better than competitors do and acting on those insights faster and more effectively.
Week 1-2: Foundation Assessment
- Audit existing customer data and touchpoint tracking capabilities
- Interview 5-10 recent customers about their experience and decision-making process
- Map current understanding of customer journey stages and transitions
- Identify highest-impact journey improvement opportunities
Week 3-4: Initial Journey Mapping
- Document one complete customer journey from awareness to advocacy
- Identify key touchpoints, decision moments, and influence factors
- Map internal processes and responsibilities to customer journey stages
- Establish baseline metrics for journey performance measurement
Week 5-6: Technology Integration
- Implement basic analytics and tracking for journey touchpoint measurement
- Set up automated workflows for journey stage transitions
- Create reporting dashboards combining CRM and journey data
- Test integration accuracy and data quality
Week 7-8: Experience Optimization
- Implement improvements for identified journey friction points
- Launch personalized content and messaging for different journey stages
- Train team members on journey-focused customer interaction approaches
- Begin measuring journey performance improvements and customer satisfaction changes
Week 9-12: Expansion and Refinement
- Extend journey mapping to additional customer segments
- Develop predictive models for journey outcome forecasting
- Implement advanced personalization and dynamic journey adaptation
- Create systematic processes for ongoing journey optimization and improvement
Remember, as we discussed in our comprehensive guide to data-driven decision making for non-technical founders, success comes from consistent application of simple principles rather than complex systems implementation.
Conclusion: The Journey Beyond Your CRM
Your CRM shows transactions, but customer journey mapping reveals transformation. It shows what customers buy, but journey mapping explains why they buy—and why they stay.
The SMEs succeeding in increasingly competitive markets aren’t necessarily those with the best products or lowest prices. They’re organizations that understand their customers’ complete experience and optimize every interaction for maximum value and satisfaction.
Customer journey mapping transforms SMEs from product sellers to experience creators, from transaction processors to relationship builders, from reactive responders to proactive partners.
The question isn’t whether customer journey mapping will become essential for SME success—it already has. The question is whether you’ll lead this transformation in your market or follow it.
Your customers are on journeys whether you map them or not. Your competitors are increasingly understanding those journeys and optimizing their experiences accordingly.
The choice, as always, is yours. But the time for that choice is now.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How does customer journey mapping differ from CRM analytics? A: CRM analytics track what customers do (transactions, interactions, behaviors). Journey mapping explains why they do it, what influences their decisions, and how to optimize their experience for better outcomes.
Q: What’s the minimum viable approach for SME journey mapping? A: Start with one customer segment and map their journey from first awareness to advocacy. Focus on major touchpoints and decision moments before capturing every interaction. Basic journey mapping is better than perfect mapping that never gets implemented.
Q: How long does it take to see results from customer journey mapping? A: Most SMEs see immediate insights from initial customer interviews and journey documentation. Measurable improvements in conversion rates and customer satisfaction typically appear within 60-90 days of implementing journey-based optimizations.
Q: Can journey mapping work for B2B SMEs with complex sales processes? A: Yes, especially for B2B SMEs. Complex sales processes involve multiple stakeholders and extended decision cycles that CRMs handle poorly but journey mapping illuminates clearly. B2B journey mapping often provides the highest ROI due to complex decision dynamics.
Q: What’s the biggest mistake SMEs make with customer journey mapping? A: Mapping from internal operational perspective rather than customer experience reality. Successful journey mapping requires actual customer input through interviews, surveys, and behavior analysis rather than internal assumptions about customer experiences.
Q: How do you measure customer journey mapping ROI? A: Track improvements in key metrics like customer acquisition cost, conversion rates, customer lifetime value, and churn reduction. Most SMEs see 15-30% improvement in these metrics within six months of implementing comprehensive journey mapping.
Q: Do I need expensive software for effective journey mapping? A: Not necessarily. Many successful SME journey mapping initiatives start with spreadsheets, customer interviews, and basic analytics tools. Technology should support your understanding, not create it. Start simple and add sophistication as your journey mapping capability matures.
Ready to see beyond what your CRM shows and understand the complete customer experience driving your business success? At Pivot BI Analytics LLC, we specialize in helping SMEs implement customer journey mapping that transforms operational data into customer experience insights. Our JOURNEY framework has helped 200+ SMEs increase customer lifetime value by 67% while reducing acquisition costs by 34%.
Contact us today for a complimentary Customer Journey Assessment designed specifically for SMEs ready to understand what their CRM can’t see—and optimize the complete customer experience driving their business growth.
This transformation from transaction tracking to experience understanding isn’t just about better customer service—it’s about creating sustainable competitive advantages through deeper customer relationships and more effective resource allocation.
The journey to customer understanding starts with a single step. The question is: will you take that step today, or will your competitors map your customers’ journeys first?
