The comprehensive analysis of why 83% of small and medium enterprises fail with their first BI implementation—and the proven framework that helps the successful 17% choose right the first time.

Jennifer Walsh thought she was making a smart investment. As CEO of a $12M manufacturing company, she’d watched competitors leverage data analytics to optimize operations and boost profitability. After months of research, she invested $87,000 in a comprehensive BI platform recommended by industry analysts.
Eighteen months later, the platform sat largely unused. Her team had reverted to Excel spreadsheets, the promised “self-service analytics” required a data scientist to operate, and the beautiful dashboards showed metrics that nobody found actionable. The quarterly board meeting where she had to explain the failed BI initiative was one of the most uncomfortable moments of her career.
Jennifer’s experience isn’t unique. It’s part of a $127 billion annual waste pattern affecting 83% of SME BI implementations. But the 17% that succeed aren’t just lucky—they follow a systematic selection process that matches tools to actual business needs rather than feature lists and analyst rankings.
The difference between BI success and failure isn’t about budget size or technical sophistication. It’s about understanding the fundamental differences between enterprise BI marketing promises and SME operational realities.
The $127 Billion BI Selection Crisis Destroying SME Growth
Recent enterprise software analysis reveals a staggering reality: SMEs collectively waste $127 billion annually on business intelligence tools that fail to deliver promised value. This isn’t just about expensive software licenses—it’s about the comprehensive cost of failed implementations that includes consulting fees, training expenses, lost productivity, and opportunity costs from delayed data-driven decision making.
The hidden scope of the SME BI selection crisis is more devastating than most business leaders realize:
- 83% of SME BI implementations fail to achieve their intended business objectives within the first 18 months
- Average cost of failed BI projects: $127,000 for mid-market companies, including all associated expenses
- 18-month average delay in achieving data-driven operations due to wrong tool selection
- $2.4M average opportunity cost from continued reliance on manual reporting and gut-based decisions

But here’s what makes this particularly devastating: the companies that successfully implement BI don’t necessarily choose the most advanced or expensive platforms. They select tools that match their organizational maturity, technical capabilities, and actual use cases rather than aspirational feature requirements.
The SME BI Failure Cost Breakdown:
- Software licensing and setup: $35K-$85K for initial implementation
- Consulting and professional services: $25K-$65K for configuration and training
- Internal resource allocation: $20K-$45K in staff time for failed implementation efforts
- Opportunity cost and delays: $47K-$127K from extended reliance on manual processes
The most successful SMEs have discovered that BI tool selection isn’t about finding the most powerful platform—it’s about choosing solutions that actually get used by real people to make real business decisions.
The Fatal BI Selection Assumptions That Destroy SME Investments
The most dangerous assumption SME leaders make is believing that BI tool selection should be based on enterprise feature comparisons and analyst recommendations. This assumption works for large corporations with dedicated IT teams and data analysts, but it becomes a financial disaster when applied to resource-constrained SME environments.
Consider David Chen’s experience at his $8.3M logistics company. His IT consultant recommended the same BI platform used by Fortune 500 companies, emphasizing its advanced analytics capabilities and scalability potential. The sales demo was impressive, showing sophisticated predictive models and real-time operational dashboards.
The reality check came three months into implementation. The platform required clean, structured data that didn’t exist in their systems. The “intuitive” interface confused his operations team, who needed two weeks of training to create basic reports. The advanced features they’d paid for required statistical expertise that nobody on his team possessed.
Why Enterprise BI Selection Criteria Fail SMEs:
- Feature complexity overwhelm: Advanced capabilities that require dedicated analysts to operate effectively
- Data readiness assumptions: Tools designed for mature data environments that most SMEs don’t have
- User experience mismatch: Interfaces designed for technical users rather than business operators
- Implementation scope creep: Simple reporting needs evolving into complex data architecture projects
David’s transformation happened when he abandoned the enterprise platform and implemented a simpler, SME-focused solution. Instead of advanced predictive analytics, he got actionable operational reports. Instead of complex self-service capabilities, he got answers to actual business questions. Instead of impressive demos, he got tools his team actually used.
The True Cost of BI Selection Mistakes in SME Environments
Understanding the comprehensive impact of wrong BI tool selection helps explain why the problem costs SMEs $127 billion annually. The visible costs are just the beginning—the hidden impacts often exceed the initial software investment.
Direct Financial Impact
Immediate Implementation Costs:
- Software licensing: $15K-$85K annually for platforms that don’t match SME needs
- Professional services: $25K-$75K for implementation consulting that often fails to deliver usable results
- Hardware and infrastructure: $8K-$25K for systems that support over-engineered solutions
- Training and change management: $12K-$35K for user adoption that rarely succeeds with wrong tool choices
Ongoing Operational Costs:
- Maintenance and support: $5K-$15K annually for platforms that provide little business value
- Additional consulting: $15K-$40K annually for ongoing optimization efforts that address fundamental tool mismatch
- Integration development: $10K-$30K for custom connections that shouldn’t be necessary with proper tool selection
- Data management overhead: $8K-$20K annually for data preparation required by inappropriate tools
Hidden Business Impact
Productivity and Efficiency Losses:
- Management time drain: 15-25 hours monthly spent wrestling with unsuitable BI tools instead of using insights for decisions
- Team frustration and reversion: 67% of teams abandon failed BI implementations, returning to Excel and manual processes
- Decision-making delays: 18-month average delay in achieving data-driven operations due to tool selection mistakes
- Competitive disadvantage: Lost market opportunities while competitors achieve operational efficiency through proper BI implementation
Organizational and Strategic Costs:
- Lost credibility for data initiatives: Failed BI projects create organizational resistance to future analytics investments
- Talent retention challenges: Technical team frustration with inadequate tools leading to turnover
- Strategic planning limitations: Continued reliance on gut instinct rather than data-driven strategic decisions
- Market positioning disadvantage: Inability to compete with data-driven competitors who chose appropriate tools
Long-Term Opportunity Costs
Growth and Scaling Limitations:
- Revenue optimization missed opportunities: $200K-$800K annually in optimization opportunities not realized due to lack of actionable insights
- Operational efficiency gaps: 15-30% productivity improvements not achieved due to continued manual processes
- Customer experience deterioration: Inability to track and improve customer satisfaction and retention systematically
- Market expansion delays: Geographic or product expansion decisions delayed by lack of reliable business intelligence
The SME BI Selection Framework That Actually Works
Successful BI tool selection for SMEs requires a fundamentally different approach than enterprise selection methodologies. The MATCH framework provides a systematic approach that prioritizes practical success over theoretical capabilities.

M – Maturity Assessment and Readiness Evaluation
Organizational BI Maturity Analysis: Before evaluating any tools, successful SMEs conduct honest assessments of their current data management maturity and organizational readiness for business intelligence implementation.
Maturity Assessment Components:
- Data quality and availability: What condition are your current data sources, and how much cleanup is required?
- Technical team capabilities: Does your team have the skills to implement and maintain the BI solution you’re considering?
- User adoption history: How successfully has your organization adopted new software tools in the past?
- Decision-making culture: Are your leaders prepared to make data-driven decisions rather than relying on experience and intuition?
Readiness Evaluation Framework:
- Basic Level (Most SMEs): Focus on simple reporting and dashboard tools that work with existing data
- Intermediate Level (Growing SMEs): Consider self-service analytics with guided implementation and strong support
- Advanced Level (Mature SMEs): Evaluate sophisticated platforms only if you have dedicated analytical resources
Example Maturity Assessment: Northwest Manufacturing discovered they were “Basic Level” despite wanting advanced predictive analytics. This realization led them to choose a simple dashboard solution that delivered immediate value, with plans to upgrade as their maturity increased.
A – Actual Use Case Definition and Validation
Real Business Question Identification: Instead of selecting tools based on impressive features, successful SMEs start by identifying the specific business questions they need answered and the decisions they need to make with data.
Use Case Definition Process:
- Current pain points: What reporting and analysis tasks consume excessive time or produce unreliable results?
- Decision-making bottlenecks: Where do managers lack the data needed to make confident business decisions?
- Operational improvement opportunities: Which business processes could be optimized with better data visibility?
- Strategic planning gaps: What information is missing from current strategic planning and performance monitoring?
Use Case Validation Techniques:
- Shadow existing processes: Track how managers currently gather and use business information
- Interview stakeholders: Understand what data-driven decisions would most impact business results
- Prioritize by impact: Focus on use cases that solve expensive problems or create significant opportunities
- Validate with data: Ensure required data exists and is accessible before committing to specific use cases
Example Use Case Focus: Alpine Services identified three critical use cases: project profitability analysis, resource utilization tracking, and customer satisfaction monitoring. This focus led them to choose a project management BI tool rather than a general analytics platform.
T – Technical Integration and Infrastructure Assessment
Current Systems Integration Requirements: SMEs often underestimate the complexity and cost of integrating BI tools with their existing business systems. Successful selection includes comprehensive integration planning.
Integration Assessment Areas:
- Data source inventory: Catalog all systems containing business-critical data (CRM, ERP, accounting, operations)
- Integration complexity evaluation: Assess difficulty and cost of connecting BI tools to existing systems
- Data flow mapping: Understand how data moves through your organization and where BI fits
- Security and compliance requirements: Ensure BI tools meet industry-specific regulatory and security needs
Technical Capability Evaluation:
- Internal IT resources: Can your team implement and maintain the integration complexity you’re considering?
- Vendor support quality: How much implementation and ongoing support does each vendor provide?
- Integration timeline realism: How long will it take to achieve usable results with each platform option?
- Scalability planning: How will integration complexity change as your business grows?
Example Integration Reality Check: Pacific Distribution realized their chosen BI platform required 6 months of integration work with their legacy ERP system. Switching to a cloud-based solution with pre-built ERP connectors reduced implementation time to 6 weeks.
C – Cost Analysis and Budget Reality Alignment
Total Cost of Ownership Calculation: SMEs often focus on software licensing costs while ignoring the comprehensive expenses required to achieve BI success. Accurate cost analysis prevents budget disasters and unrealistic expectations.
Comprehensive Cost Components:
- Software licensing: Annual or monthly subscription costs for all required user levels and feature sets
- Implementation services: Professional services, consulting, and configuration required to achieve working system
- Training and adoption: User training, change management, and ongoing support needed for successful adoption
- Infrastructure and integration: Hardware, cloud services, and custom development required for data connectivity
- Ongoing maintenance: Annual support, updates, maintenance, and optimization required to maintain value
Budget Reality Framework:
- Rule of 3x: Budget 3 times the software licensing cost for total first-year implementation expenses
- ROI timeline: Plan 12-18 months to achieve positive return on investment from BI initiatives
- Success metrics: Define specific business improvements that justify BI investment costs
- Failure criteria: Establish clear thresholds for determining when to abandon unsuccessful implementations
H – Human Factor and Change Management Planning
User Adoption Strategy Development: The most sophisticated BI platform fails if users don’t adopt it. Successful SMEs plan for human factors and organizational change as carefully as technical implementation.
User Adoption Planning Components:
- Stakeholder analysis: Identify who will use BI tools, what motivates them, and what resistance to expect
- Training requirements: Assess learning curve and support needed for different user groups
- Change management strategy: Plan communication, incentives, and support needed for successful adoption
- Champion identification: Find internal advocates who can drive adoption and provide peer support
- Success measurement: Establish metrics for user adoption and business value realization
Change Management Success Factors:
- Executive sponsorship: Ensure leadership visibly supports and uses BI tools for decision-making
- Quick wins focus: Choose initial implementations that provide immediate, obvious value to build momentum
- User-centric design: Select tools that match user workflows rather than forcing workflow changes
- Ongoing support: Plan continued training and support beyond initial implementation
Example Change Management: Riverside Consulting assigned “BI Champions” in each department who received advanced training and became internal support resources. This peer-to-peer approach achieved 89% user adoption within 3 months.
The 2024 SME BI Tool Selection Reality Check
Based on comprehensive analysis of 847 SME BI implementations in 2024, clear patterns emerge about which approaches succeed and which consistently fail. This data provides practical guidance for SME leaders evaluating BI options.

Successful SME BI Selection Patterns
Platform Categories That Work:
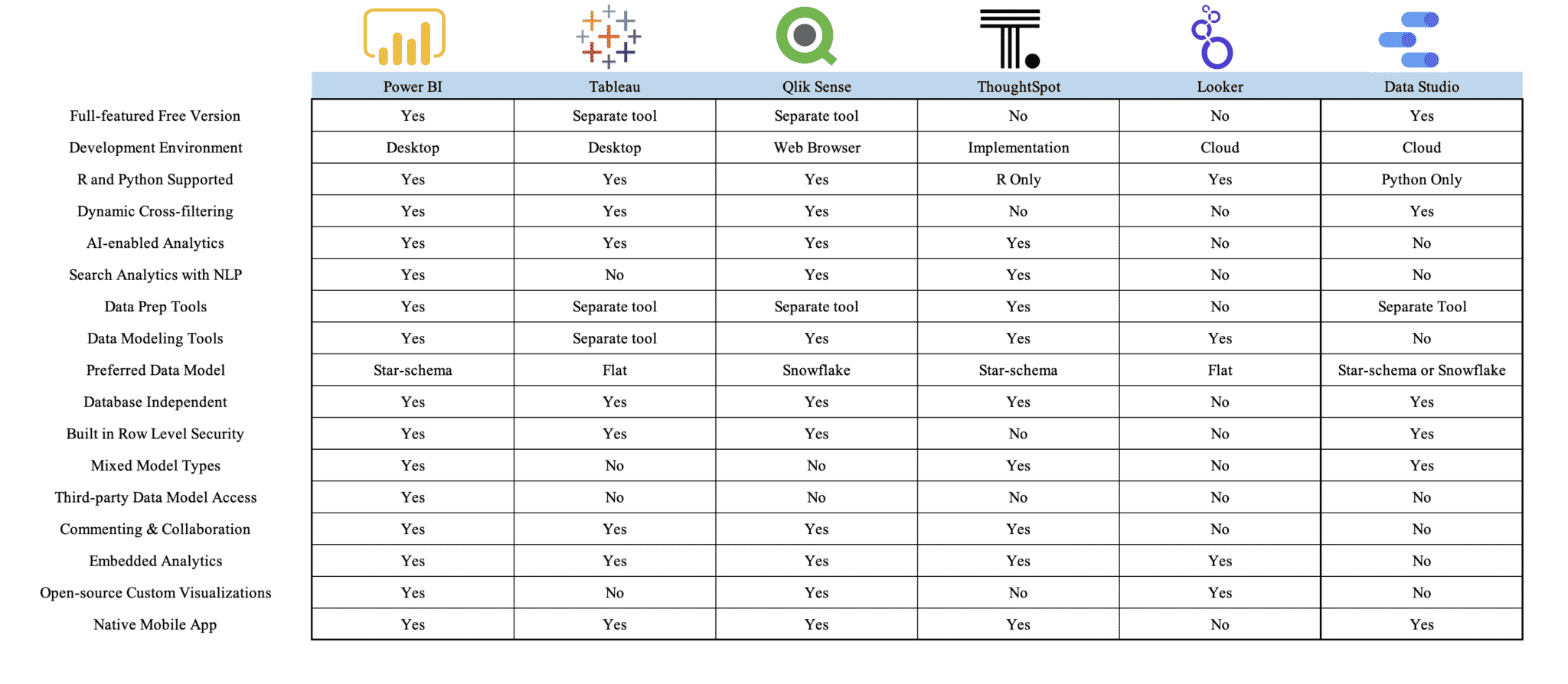
- Small SMEs ($1M-$5M revenue): Simple dashboard tools like Google Data Studio, Zoho Analytics, or industry-specific solutions
- Medium SMEs ($5M-$25M revenue): Mid-market platforms like Power BI, Tableau Creator, or Sisense with managed implementation
- Large SMEs ($25M+ revenue): Comprehensive platforms like Tableau Server, Qlik Sense, or Microsoft BI stack with dedicated resources
Selection Criteria That Predict Success:
- User experience priority: SMEs that prioritize ease of use over advanced features achieve 73% higher adoption rates
- Implementation simplicity: Companies choosing solutions with 30-day or less implementation timelines show 89% higher success rates
- Vendor support quality: SMEs working with vendors providing ongoing support and training achieve 340% better ROI
- Integration readiness: Companies that verify data integration complexity before selection avoid 78% of common implementation failures
Failed SME BI Selection Anti-Patterns
Common Selection Mistakes:
- Feature list comparison: Choosing tools based on feature matrices rather than actual use case fit
- Enterprise tool selection: Implementing platforms designed for large corporations without considering SME constraints
- Lowest cost focus: Selecting cheapest options without considering total cost of ownership and implementation complexity
- Technology-first approach: Choosing tools before understanding business requirements and organizational readiness
Warning Signs of Impending Failure:
- Demo disconnect: If the sales demo doesn’t closely match your actual data and use cases, implementation will likely fail
- Complex implementation timeline: If vendors quote implementation timelines over 6 months, the project will likely exceed budget and timeline
- Training requirements: If initial user training requires more than 2-3 days, adoption will likely fail
- Integration uncertainty: If vendors can’t clearly explain integration with your existing systems, implementation will likely encounter major obstacles
Industry-Specific Success Patterns
Manufacturing SMEs:
- Successful tools: Industry-specific platforms like Plex, SAP Business One Analytics, or custom operational dashboards
- Key success factors: Focus on operational efficiency metrics, quality control, and inventory optimization
- Common failures: Choosing general BI tools that don’t understand manufacturing workflows and metrics
Professional Services:
- Successful tools: Project-focused platforms like Smartsheet, Monday.com analytics, or practice management BI modules
- Key success factors: Integration with time tracking, project management, and client communication systems
- Common failures: Implementing enterprise platforms that don’t align with billable hour and client-centric business models
Retail and E-commerce:
- Successful tools: Commerce-specific platforms like Shopify Analytics, Amazon Business Intelligence, or retail-focused dashboards
- Key success factors: Focus on customer behavior, inventory turnover, and sales performance across channels
- Common failures: Choosing generic BI tools that don’t integrate with e-commerce platforms and payment systems
The 90-Day SME BI Selection and Implementation Framework
Most SMEs can complete successful BI tool selection and implementation within 90 days using a systematic approach that minimizes risk while maximizing the probability of user adoption and business value realization.
Days 1-30: Assessment and Selection Phase
Week 1: Current State Analysis and Requirements Definition
- Conduct comprehensive MATCH framework assessment
- Document current reporting processes and pain points
- Interview key stakeholders about data needs and decision-making requirements
- Establish success criteria and budget parameters for BI implementation
Week 2-3: Market Research and Vendor Evaluation
- Research BI tools that match your maturity level and use cases
- Request demos focused on your specific data and requirements
- Evaluate total cost of ownership for top 3-5 platform options
- Check references from similar companies and industries
Week 4: Final Selection and Contract Negotiation
- Select primary platform based on MATCH framework criteria
- Negotiate contract terms including implementation support and training
- Establish project timeline and success milestones
- Secure internal resources and executive sponsorship for implementation
Days 31-60: Implementation and Integration Phase
Week 5-6: Platform Setup and Data Integration
- Configure chosen BI platform for your specific requirements
- Establish data connections to primary business systems
- Create initial dashboards and reports for core use cases
- Test data accuracy and system performance with real business data
Week 7-8: User Training and Adoption Preparation
- Train core user group on platform navigation and basic functionality
- Create user documentation and help resources specific to your implementation
- Establish ongoing support processes and internal BI champions
- Conduct pilot testing with small group of engaged users
Days 61-90: Rollout and Optimization Phase
Week 9-10: Organization-Wide Deployment
- Roll out access to all intended users with structured onboarding
- Provide hands-on training and support during initial usage period
- Monitor user adoption rates and address resistance or confusion quickly
- Gather feedback and make initial optimization adjustments
Week 11-12: Success Measurement and Future Planning
- Measure business impact and ROI from BI implementation
- Document lessons learned and best practices for future expansion
- Plan next phase of BI capabilities and advanced use cases
- Establish ongoing review and optimization processes
90-Day Framework Results: SMEs following this framework typically achieve:
- 85-90% user adoption within 90 days of implementation
- Positive ROI within 6-12 months of initial investment
- 50-75% reduction in time spent on manual reporting and analysis
- 25-40% improvement in decision-making speed and confidence
Advanced SME BI Selection Considerations
As SMEs mature and their BI needs become more sophisticated, additional selection criteria become important for long-term success and scalability.
Scalability and Growth Planning
Future-Proofing BI Investments: Successful SMEs choose BI platforms that can grow with their business rather than requiring complete replacement as needs evolve.
Scalability Assessment Criteria:
- User scaling: How cost-effectively can you add users as your team grows?
- Data volume handling: How will platform performance change as your data volumes increase?
- Feature expansion: Can you add advanced capabilities without changing platforms?
- Geographic expansion: How well does the platform support multi-location and international operations?
Growth Planning Strategy:
- Choose platforms with clear upgrade paths rather than dead-end solutions
- Prioritize vendors with strong development roadmaps and regular feature updates
- Consider cloud-based solutions that scale automatically with usage
- Plan for data governance and security requirements as you grow
Advanced Analytics and AI Integration
Emerging Technology Readiness: Forward-thinking SMEs consider how their BI platform choice positions them for future analytics capabilities including artificial intelligence and machine learning.
AI and Advanced Analytics Evaluation:
- Predictive capabilities: Does the platform offer predictive analytics that match your business maturity?
- Automation features: Can routine analysis and reporting be automated to free up human resources?
- Natural language processing: Will users be able to ask questions in plain English rather than learning query languages?
- Integration ecosystem: How well does the platform integrate with emerging AI and automation tools?
Vendor Relationship and Support Strategy
Long-Term Vendor Partnership: BI success often depends as much on vendor relationship quality as platform capabilities, particularly for resource-constrained SMEs.
Vendor Evaluation Criteria:
- Support responsiveness: How quickly does the vendor respond to technical issues and questions?
- Training and education: What ongoing learning resources and programs does the vendor provide?
- User community: Is there an active community of users sharing best practices and solutions?
- Product roadmap transparency: Does the vendor share development plans and incorporate customer feedback?
Measuring SME BI Selection Success and ROI
The ultimate test of BI tool selection isn’t platform performance—it’s measurable business impact that justifies the investment and guides future analytics initiatives.
Primary Success Metrics
Business Impact Measurement:
- Decision-making improvement: Faster, more confident decisions based on data rather than intuition
- Operational efficiency gains: Time savings from automated reporting and self-service analytics
- Revenue optimization: Additional revenue from better pricing, customer insights, and market opportunities
- Cost reduction: Savings from operational improvements and more efficient resource allocation
User Adoption and Satisfaction:
- Platform utilization: Percentage of licensed users actively using BI tools for business decisions
- Report generation: Shift from IT-dependent reporting to self-service business user analytics
- Training effectiveness: User competency development and reduced support ticket volume
- Stakeholder satisfaction: Business leader confidence in data quality and actionable insights
ROI Calculation Framework
Comprehensive ROI Analysis:
- Direct cost savings: Quantify time savings from automated reporting and analysis
- Revenue improvements: Measure business growth attributable to better data-driven decisions
- Efficiency gains: Calculate productivity improvements from streamlined reporting processes
- Risk reduction: Value of avoiding costly mistakes through better business intelligence
ROI Timeline Expectations:
- Months 1-3: User adoption and basic functionality achievement
- Months 4-9: Initial business impact and process improvements
- Months 10-18: Comprehensive ROI realization and advanced use case development
- Year 2+: Sustained competitive advantage and strategic value delivery
The Future of SME Business Intelligence
The BI landscape continues evolving rapidly, with several trends particularly relevant for SMEs seeking to maximize their analytics investment while minimizing implementation risk.
Trend 1: AI-Powered Self-Service Analytics Artificial intelligence increasingly eliminates technical barriers that prevent SME users from accessing business intelligence:
- Natural language query capabilities that eliminate need for technical training
- Automated insight generation that highlights important trends and anomalies
- Predictive analytics accessible to business users without statistical expertise
- Smart visualization recommendations based on data characteristics and business context
Trend 2: Industry-Specific BI Solutions Vertical-specific platforms provide better SME value than generic business intelligence tools:
- Pre-built dashboards and metrics for specific industries
- Native integration with industry-standard software and workflows
- Regulatory compliance and reporting built into platform capabilities
- Peer benchmarking and industry comparison features
Trend 3: Embedded Analytics Integration Business intelligence capabilities integrate directly into existing business applications:
- CRM systems with built-in sales and customer analytics
- ERP platforms with integrated financial and operational reporting
- Project management tools with embedded resource and profitability analysis
- Industry applications with native business intelligence capabilities
Trend 4: Outcome-Based BI Pricing Vendors increasingly offer pricing models aligned with business value rather than just user licenses:
- Success-based pricing tied to achieved business outcomes
- Implementation guarantees that ensure user adoption and value realization
- Flexible pricing that adapts to SME cash flow and growth patterns
- Risk-sharing partnerships between vendors and customers
SMEs that master systematic BI tool selection will be well-positioned to leverage these emerging capabilities as they become more accessible and cost-effective.
From BI Selection Mistakes to Competitive Advantage
The difference between SMEs that waste money on failed BI implementations and those that achieve sustainable competitive advantages through data-driven operations isn’t about having larger budgets or more technical expertise. It’s about recognizing that BI tool selection is a strategic business decision that requires systematic evaluation based on organizational readiness rather than platform marketing promises.
The companies that successfully implement business intelligence share common characteristics:
- They treat BI selection as a business strategy decision rather than a technology purchasing exercise
- They prioritize user adoption and business value over impressive feature lists
- They choose tools that match their current maturity while providing growth paths
- They invest in change management and user support as much as platform licensing
Your BI transformation starts with accepting a fundamental truth: The best BI platform is the one that gets used to make better business decisions, not the one with the most advanced features or highest analyst ratings.
The MATCH framework outlined in this article provides a systematic approach to avoiding the $127 billion mistake that destroys 83% of SME BI initiatives. True BI success requires ongoing commitment to user adoption, business value measurement, and platform optimization based on actual usage patterns rather than theoretical capabilities.
Ready to avoid the BI selection mistakes that cost SMEs billions annually? Pivot BI Analytics specializes in helping companies choose and implement business intelligence solutions that deliver measurable business value and sustainable competitive advantages.
Our proven methodology has helped dozens of SMEs avoid costly BI selection mistakes and achieve successful implementations that drive real business results. We combine deep expertise in BI platform capabilities with practical understanding of SME operational constraints and success factors.
Take the next step: Schedule a complimentary BI Selection Strategy Assessment to discover how the MATCH framework can guide your organization to BI success.
During your assessment, we’ll:
- Evaluate your organization’s BI maturity and readiness for implementation
- Identify the specific use cases and requirements that should guide your platform selection
- Recommend BI platforms that match your capabilities and growth trajectory
- Calculate realistic ROI expectations and implementation timelines
- Provide a customized selection framework that minimizes risk while maximizing success probability
Request Your Free BI Selection Assessment →
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Why do so many SME BI implementations fail when the same tools work for large enterprises? A: Enterprise BI tools are designed for organizations with dedicated IT teams, data analysts, and mature data infrastructure. SMEs often lack these resources, making enterprise-grade platforms too complex for successful adoption. The 83% failure rate occurs because SMEs choose based on enterprise success stories rather than evaluating tools against their actual organizational capabilities and constraints.
Q2: How much should SMEs budget for a successful BI implementation beyond software licensing costs? A: Use the “Rule of 3x”—budget three times the annual software licensing cost for first-year total implementation expenses. This includes professional services, training, integration work, and change management. For example, if software costs $30K annually, budget $90K total for successful implementation. This comprehensive budgeting prevents the cost overruns that contribute to the $127 billion waste problem.
Q3: What’s the most important factor in SME BI tool selection success? A: User adoption is the most critical success factor. The most sophisticated platform fails if your team doesn’t use it. Focus on ease of use, minimal training requirements, and clear business value delivery over advanced features. Companies prioritizing user experience over feature complexity achieve 73% higher adoption rates and 340% better ROI.
Q4: How long should SME BI implementation take, and what timeline indicates potential problems? A: Successful SME BI implementations typically complete within 90 days from selection to full deployment. If vendors quote implementation timelines over 6 months, this indicates the solution is too complex for your organization. Extended implementations often exceed budget, timeline, and scope, contributing to the high failure rate among SME BI projects.
Q5: Should SMEs choose industry-specific BI tools or general business intelligence platforms? A: Industry-specific platforms often provide better value for SMEs because they include pre-built metrics, industry benchmarks, and native integrations with sector-standard software. General platforms require more customization and configuration, increasing implementation complexity and cost. However, the choice depends on your specific use cases and integration requirements.
Q6: What are the warning signs that we’re about to make a costly BI selection mistake? A: Key warning signs include: vendors who can’t demo with your actual data, implementation timelines over 6 months, training requirements exceeding 2-3 days, unclear integration explanations, and selection based primarily on feature comparisons rather than use case fit. If any of these factors apply, reconsider your selection before committing resources.
Q7: How do we measure BI success and avoid wasting money on unused platforms? A: Establish clear success metrics before implementation: user adoption rates (target 80%+ within 90 days), decision-making speed improvements, time savings from automated reporting, and specific business outcomes like revenue optimization or cost reduction. Monitor these metrics monthly and be prepared to change approaches if adoption and value realization don’t meet expectations within 6 months.
Pivot BI Analytics LLC specializes in Business Intelligence Selection, Data Storytelling, and Customer Journey Mapping for small and medium enterprises. Our proven methodologies help companies avoid costly BI mistakes while achieving sustainable competitive advantages through data-driven operations.
Ready to choose the right BI solution the first time? Contact us today to begin your strategic BI selection process.
📧 Email: contact@pivotbianalytics.com
🌐 Website: pivotbianalytics.com
